Headless
How to approach headless in DynamicWeb 10.
A headless implementation separates the frontend and backend of a DynamicWeb solution. Instead of rendering pages using Razor templates, all content and commerce data is delivered through the DynamicWeb Delivery API (/dwapi/).
This gives developers the freedom to build completely decoupled applications using their preferred frontend frameworks — React, Vue, Angular, Svelte, or even native mobile frameworks like Flutter.
In a headless setup:
- DynamicWeb acts as a service: It handles CMS, Commerce, and PIM, and exposes content and data via APIs
- Your app is independent: The frontend is a standalone application, hosted wherever you want (CDN, cloud service, container platform)
- Communication is API-based: The app fetches content, product data, carts, and user context through REST endpoints
This approach ensures a clean separation of concerns: DynamicWeb manages content and commerce logic, while the frontend focuses entirely on user experience and design.
Hosting a Headless Implementation
A headless implementation always consists of at least two parts:
DynamicWeb installation
- Hosts all content, product data, and business logic.
- Exposes the Delivery API (
/dwapi). - Can be run in the Dynamicweb Cloud for scalability and automatic updates.
Decoupled frontend app
- A standalone app built with your chosen framework.
- Contains JavaScript, CSS, and static assets.
- Can be hosted anywhere: Cloud services (Azure, AWS, GCP), CDN platforms (Netlify, Vercel, Cloudflare Pages), or traditional hosting or containers
Because the app is fully decoupled, it can live outside the DynamicWeb environment while still consuming its data and services.
Example: Retrieving a BlogPost page using the delivery API
All content in DynamicWeb is exposed to the frontend via ViewModels - traditional DynamicWeb implementations uses Razor templates to render the markup on the server.
However, instead of injecting ViewModels into a template and rendering the markup on the server, DynamicWeb also exposes the data via a full featured REST-based web API.
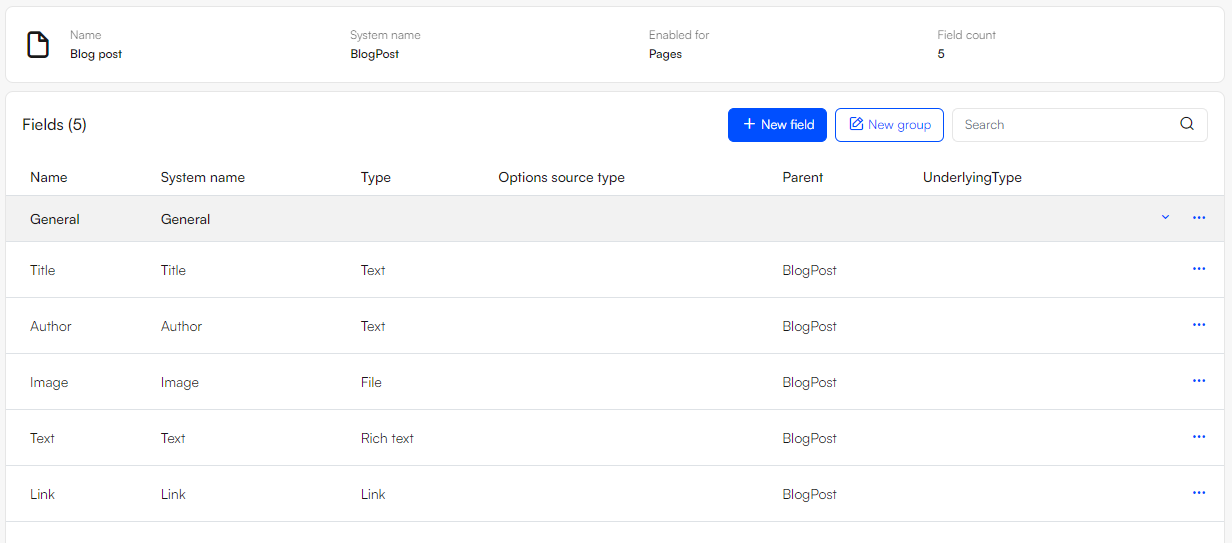
As an example, let's say we have created an item type called "BlogPost" and create a page using this item type.
The BlogPost item type have these fields:
- Title
- Author
- Image
- Text
- Link
Once created, a BlogPost-page can be retrieved using the delivery API by requesting the page by its ID:
GET https://yoursolution.url/dwapi/content/pages/13
The ViewModel is then returned as a json document that can be used to render the blogpost using a JS component.
{
"id": 13,
"name": "My blog post",
"createdDate": "2023-06-14T13:32:34.873",
"updatedDate": "2023-06-14T13:45:22.1844074+02:00",
"title": null,
"description": null,
"keywords": "",
"areaID": 1,
"path": [
{
"id": 3,
"name": "About us"
},
{
"id": 13,
"name": "My blog post"
}
],
"languages": [],
"item": {
"fields": [
{
"name": "Title",
"systemName": "Title",
"value": "My blog post"
},
{
"name": "Author",
"systemName": "Author",
"value": "Nicolai Pedersen"
},
{
"name": "Image",
"systemName": "Image",
"value": [
{
"extension": ".png",
"name": "contentarea.png",
"path": "/Files/Images/ExampleImages/contentarea.png",
"focalX": 0,
"focalPositionFromLeft": 50,
"focalY": 0,
"focalPositionFromTop": 50,
"pathUrlEncoded": "%2FFiles%2FImages%2FExampleImages%2Fcontentarea.png"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Text",
"systemName": "Text",
"value": "<h2>Simplify eCommerce</h2>\n<p>DynamicWeb is PIM, eCommerce, Marketing and CMS in one powerful Commerce Suite featuring standard integrations to Microsoft Dynamics ERP.</p>\n<div>\n<p>Create an omnichannel B2B, B2C or D2C commerce experience using a modern <a href=\"https://dynamicweb.com/technology/mach\">MACH based application</a>, enabling you to build, run and scale your business the way you want.</p>\n</div>"
},
{
"name": "Link",
"systemName": "Link",
"value": {
"pageId": 5,
"paragraphId": 0,
"url": "/contact",
"isExternal": false
}
}
],
"id": "1",
"systemName": "BlogPost",
"pageID": 13,
"paragraphID": 0,
"link": "/about-us/my-blog-post"
},
"propertyItem": null
}
Using React to do something with this data could look like this:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react";
function BlogPost({ pageId }) {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
// Fetch page data from the Dynamicweb Delivery API
fetch(`https://localhost:6001/dwapi/content/pages/${pageId}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((json) => {
setData(json);
setLoading(false);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error("Failed to fetch data", err);
setLoading(false);
});
}, [pageId]);
if (loading) return <p>Loading...</p>;
if (!data) return <p>Could not load blog post.</p>;
// Extract fields for easier access
const fields = data.item.fields.reduce((acc, f) => {
acc[f.systemName] = f.value;
return acc;
}, {});
return (
<article className="blog-post">
<h1>{fields.Title}</h1>
<p className="author">Written by {fields.Author}</p>
{Array.isArray(fields.Image) && fields.Image.length > 0 && (
<img
src={fields.Image[0].path}
alt={fields.Title}
style={{ maxWidth: "100%", height: "auto" }}
/>
)}
<section
className="content"
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: fields.Text }}
/>
{fields.Link && (
<p>
<a href={fields.Link.url}>Read more</a>
</p>
)}
</article>
);
}
export default BlogPost;
/* Use in app */
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import BlogPost from "./BlogPost";
ReactDOM.render(<BlogPost pageId={13} />, document.getElementById("root"));
Development and frameworks
In headless implementations you can use any JS framework and development tool stack you desire.
An example of development stack:
- Git
- VS Code
- Node
- NPM
- Webpack/Vite/Esbuild, ESlint etc.
Some of the more popular frameworks for implementing headless are:
- React
- Vue
- Next.js
- Nuxt.js
- Angular
- Flutter - for developing native apps using data from DynamicWeb
Things to consider
In a regular DynamicWeb implementation using server side rendered, you are operating in a stateful context where the DynamicWeb application keeps track of the context and state of the current visitor.
When implementing in headless you are operating in a stateless context - this shifts a lot of responsibility to the frontend app which must keep track of things like:
- URLs and History
- User logins
- Carts
- Chosen language
- Chosen currency
- Chosen delivery country
- Impersonation rules
All in all, headless is the right choice when:
- You want maximum control of the frontend experience
- Your project involves apps or multi-channel delivery
- You have a strong frontend team comfortable with modern stacks
- Integration with other microservices is a priority